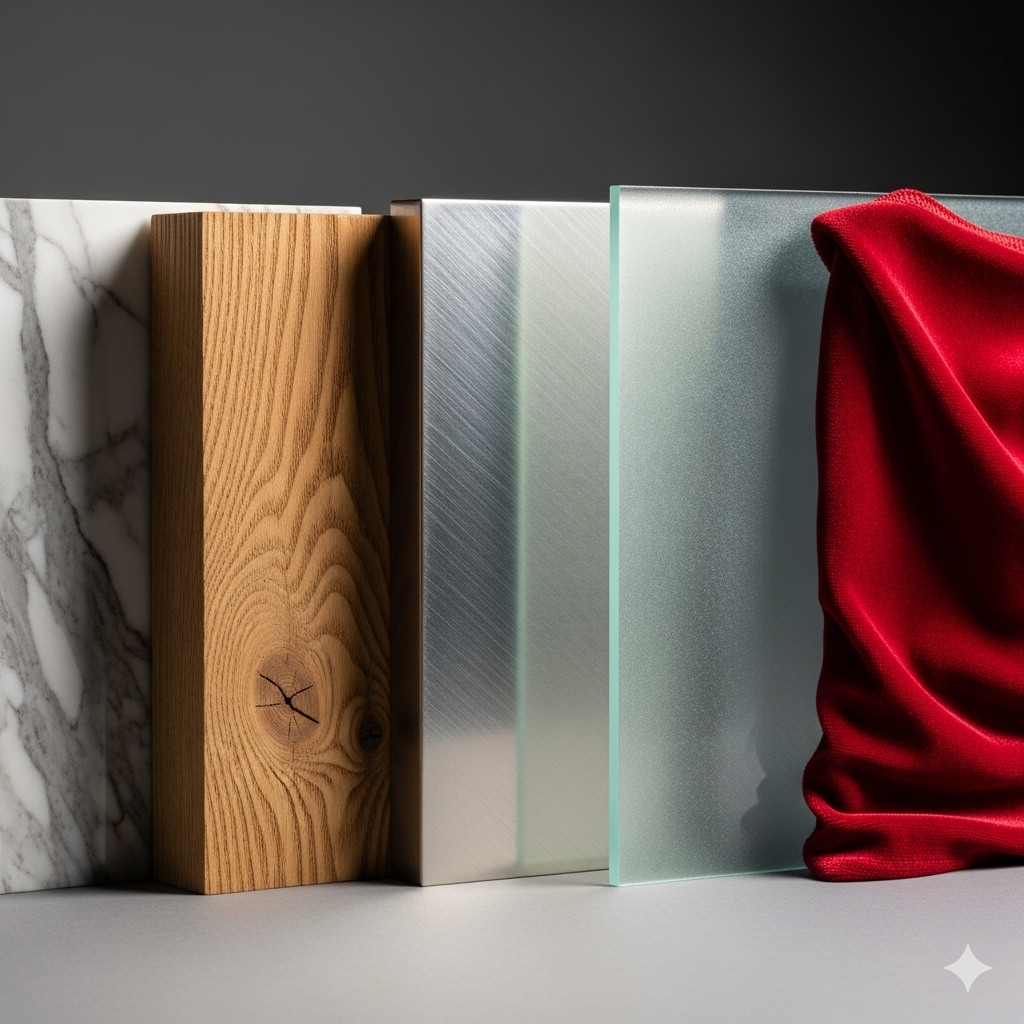
Material Comparisons in Interior Design – Wood, Laminates, Veneers, Glass, and Metal Explained
Every dream home begins with the right choice of materials. Interior design is not only about aesthetics but also about durability, functionality, and long-term value. When homeowners begin their journey, they often face confusion between wood, laminates, veneers, glass, and metal. Each of these materials has its unique advantages, limitations, and applications. Understanding these differences through material comparisons can help you make informed decisions that blend beauty with practicality.
The choice of material impacts cost, maintenance, lifespan, and even the vibe of your interiors. For example, wood is timeless and elegant but expensive; laminates are affordable and versatile but lack authenticity; glass adds openness and luxury but needs regular upkeep; metal brings strength and industrial appeal but may not suit all tastes. This detailed guide will take you through in-depth material comparisons to ensure you select the best fit for your design vision.
Table of Contents
Confused about which material suits your project?
Connect with InteriorGrid.com experts for tailored guidance.
Wood: The Classic Foundation
Wood has long been regarded as the foundation of timeless interior design, admired for its unmatched warmth, richness, and natural charm. Its use spans centuries, from intricately carved furniture in traditional homes to sleek, contemporary panels and flooring in modern interiors. In terms of material comparisons, wood is often seen as the premium choice due to its remarkable durability, structural strength, and ability to age gracefully. High-quality hardwoods such as teak, oak, and walnut not only provide longevity but also develop a unique patina over time, enhancing the aesthetic value of interiors.
Wood’s versatility makes it suitable for a wide range of applications: solid wood flooring brings an elegant, warm base to living spaces; furniture pieces like cabinets, beds, and dining sets showcase craftsmanship; and wall paneling or ceiling beams add depth and character to rooms. Additionally, wood is eco-friendly when sourced sustainably, contributing to greener building practices and healthier living environments.
However, premium quality comes at a price—wood is generally more expensive than laminates, veneers, or engineered alternatives, and it requires regular maintenance such as polishing, termite protection, and moisture control to retain its beauty and longevity. Despite these considerations, wood continues to be the preferred material for those seeking interiors that combine timeless appeal, functionality, and a natural connection to the living environment, making it a benchmark in material comparisons for interior projects.
Advantages of Wood:
- Material Comparisons – Understanding the Value of Natural Materials vs. Synthetics
- When it comes to Material Comparisons, homeowners and designers often weigh natural materials against synthetic alternatives. Material Comparisons highlight how natural materials like wood, stone, and marble are long-lasting and durable if maintained well, making them ideal for interiors that demand both functionality and beauty. Unlike synthetics, natural materials can be polished, carved, and customized to suit a wide variety of design preferences.
- Through detailed Material Comparisons, it becomes clear that natural materials add luxury and a natural vibe to interiors, creating warmth, texture, and character that synthetics often struggle to replicate. While laminates and engineered surfaces offer affordability and convenience, Material Comparisons show that solid wood or natural stone holds better resale value. This is because buyers and tenants recognize the prestige and longevity associated with natural finishes.
- In Material Comparisons, one of the strongest arguments for natural materials lies in their versatility. Wood, for instance, can be refinished multiple times, while stone surfaces age gracefully, developing character over the years. On the other hand, synthetics like laminates or engineered quartz may require less maintenance but lack the timeless appeal revealed through consistent Material Comparisons.
- For designers and homeowners, Material Comparisons serve as a guide to balance aesthetics, cost, and practicality. Where budget and speed are priorities, synthetics stand out. But in premium homes, Material Comparisons consistently show natural choices like teak, oak, granite, or marble are unrivaled in terms of luxury, resale potential, and long-term value.
- Ultimately, Material Comparisons reinforce the idea that while synthetics bring efficiency, natural materials bring prestige, customization, and longevity—qualities that often outweigh the upfront savings of artificial alternatives. For modern interiors, relying on Material Comparisons ensures smarter decisions that align with lifestyle, budget, and design goals.
Limitations of Wood:
- When homeowners and designers consider Material Comparisons, one of the most discussed debates is between natural wood and engineered alternatives like laminates and veneers. Through repeated Material Comparisons, it becomes clear that natural wood offers unmatched elegance, durability, and prestige, but it also comes with unique challenges that must be weighed carefully.
- In detailed Material Comparisons, the first factor that often stands out is cost. Natural wood is generally expensive compared to laminates and veneers, which are designed to provide a budget-friendly alternative. These Material Comparisons highlight that while laminates and veneers allow wider accessibility to stylish interiors, natural wood is reserved for those willing to invest in luxury and longevity.
- Another recurring theme in Material Comparisons is the vulnerability of natural wood. Unlike synthetics, untreated wood is susceptible to termites and moisture damage if untreated. In these Material Comparisons, we see that while laminates and veneers offer greater resistance to pests and dampness, they do not deliver the same organic charm or tactile richness that wood provides.
- Maintenance also becomes a key factor in Material Comparisons. Natural wood requires periodic maintenance like polishing, refinishing, or sealing to retain its shine and durability. Laminates, by contrast, demand minimal care, making them appealing in Material Comparisons focused on convenience and low upkeep.
- Despite the drawbacks revealed in Material Comparisons, natural wood maintains a higher resale and emotional value. Buyers and design-conscious homeowners consistently prefer wood for its warmth, character, and ability to age gracefully. Laminates and veneers, though practical, rarely inspire the same sense of timeless luxury in Material Comparisons.
- Ultimately, Material Comparisons demonstrate that the choice between wood and synthetics depends on priorities—budget, maintenance, lifestyle, and design goals. Where efficiency and cost-saving dominate, laminates and veneers win. But in Material Comparisons where prestige, customization, and long-term investment matter most, natural wood remains the undeniable leader.
- By relying on repeated Material Comparisons, homeowners can make informed decisions that balance aesthetics, durability, and practicality. These Material Comparisons ensure clarity, helping families and designers align material choices with the realities of daily life and long-term expectations.
Applications: Dining tables, wardrobes, doors, bed frames, wall paneling, flooring.
Wood remains the go-to for homeowners who want authenticity, but it comes with the cost of maintenance and budget considerations.
Laminates: Affordable and Stylish
Laminates are engineered sheets made from kraft paper or cellulose bonded with resin, offering a budget-friendly and versatile alternative to solid wood. Commonly used in modular furniture, cabinetry, wardrobes, and wall panels, laminates are valued for their affordability, durability, and low maintenance.
They come in a wide range of textures, colors, and finishes—from wood-grain and stone looks to glossy or matte styles—allowing designers to achieve premium aesthetics on a budget. Laminates are also scratch, stain, and moisture-resistant, making them ideal for high-traffic areas like kitchens and offices. Lightweight and easy to install, they save both time and labor during projects.
Despite their low cost, laminates can create a high-end look when paired with quality hardware, making them a smart choice for modern interiors where style, functionality, and cost need to align.
Advantages of Laminates:
- Highly Affordable and Widely Available
- Laminates are one of the most budget-friendly materials used in modern interiors. Their affordability makes them an attractive choice for homeowners who want stylish finishes without overspending. Being mass-produced and widely available across markets, laminates ensure quick sourcing and consistency in design, which is particularly helpful in large-scale projects.
- Comes in Hundreds of Designs, from Matte to Glossy Finishes
- One of the biggest advantages of laminates is the sheer variety of finishes. From matte surfaces that give a subtle and elegant look to glossy laminates that bring vibrancy and brightness, the range is virtually endless. Laminates also replicate wood grains, stone textures, or abstract patterns, allowing designers to achieve premium looks at a fraction of the cost.
- Resistant to Scratches and Stains
- Durability is another reason laminates are so popular. Unlike wood or veneer, they are designed to resist scratches and stains, making them ideal for high-traffic areas like kitchens, wardrobes, and office furniture. This resistance helps maintain a polished look over time, even with everyday wear and tear.
- Easy to Clean and Maintain
- For families with kids or busy lifestyles, laminates are extremely practical. A simple wipe with a damp cloth is usually enough to clean them, with no need for polishing or special treatments. Their low-maintenance nature makes them perfect for spaces where hygiene and quick cleaning are priorities, such as kitchens and study tables.
Limitations of Laminates:
- Lacks the Authenticity of Natural Wood
- While laminates can replicate the appearance of wood, stone, or other premium materials, they do not have the natural warmth, depth, or grain variations that real wood offers. For homeowners who value authenticity and a truly organic vibe, laminates may feel slightly artificial compared to the richness of natural timber or high-quality veneers.
- Once Damaged, Cannot Be Repaired – Needs Replacement
- One of the biggest drawbacks of laminates is their non-repairable nature. If a laminate sheet gets chipped, cracked, or swollen due to moisture, it cannot be restored like wood, which can be sanded or polished. The only solution is a full replacement of the affected panel, which can be inconvenient and sometimes costly in the long run.
- Lower Lifespan Compared to Wood and High-Quality Veneers
- Although laminates are durable and resistant to scratches and stains, they generally have a shorter lifespan than solid wood or top-grade veneers. Over time, laminates may show signs of wear, fading, or peeling, especially in high-use areas like kitchens and wardrobes. In material comparisons, laminates are best seen as a functional, short-to-medium-term solution rather than a lifetime investment like wood.
Applications: Kitchen cabinets, wardrobes, TV units, study tables, office furniture.
For cost-effective interiors, laminates are often the first choice. They make premium-looking designs accessible for everyday homeowners.
Veneers: Natural Beauty on a Budget
Veneers are thin layers of natural wood that are carefully sliced and adhered to substrates like plywood, MDF, or particleboard, offering a cost-effective way to enjoy the elegance of solid wood. In material comparisons, veneers occupy a middle ground between solid wood and laminates, combining authentic natural textures with affordability and versatility.
One of the key advantages of veneers is that they retain the natural grains, patterns, and warmth of wood, giving furniture, cabinets, and wall panels a luxurious and premium appearance without the high expense of solid timber. Homeowners can enjoy customized finishes, rich textures, and a wide variety of wood species—from oak and walnut to teak—while keeping overall costs lower than pure wood options.
Veneers are also lighter than solid wood, which makes them easier to handle, transport, and install. In addition, they can be polished, stained, or treated to achieve different finishes, allowing interior designers to match specific color palettes or design themes. Compared to laminates, veneers offer more authenticity and visual appeal, although they may require slightly higher maintenance to prevent moisture damage or scratches.
Another benefit of veneers is their sustainability factor. Using thin slices of wood rather than solid blocks conserves timber resources, making them a more eco-conscious choice for modern interior projects. Overall, in material comparisons, veneers provide an excellent balance of aesthetic value, cost-effectiveness, and functional practicality, making them a preferred choice for premium yet budget-conscious interiors.
Advantages of Veneers:
- Retains the Authentic Look of Real Wood
- Veneers are made by slicing thin layers of natural wood and applying them onto a base material like MDF or plywood. This ensures that they retain the authentic look, texture, and grain patterns of real wood, offering interiors a premium and organic feel. Unlike laminates, veneers provide a natural warmth and richness that cannot be replicated synthetically.
- More Affordable than Solid Wood
- One of the biggest benefits of veneers is that they deliver the luxury of real wood at a fraction of the cost. Since only a thin slice of timber is used, veneers are much more economical than using solid wood across large furniture or wall paneling projects. This makes them a cost-effective option for achieving elegance without overspending.
- Can Be Polished to Change Appearance Over Time
- Veneers have the flexibility to be re-polished or re-stained, allowing homeowners to refresh or completely change the look of their interiors over time. This adaptability not only extends their lifespan but also supports evolving design trends or personal style preferences, something laminates cannot offer.
- Lightweight Compared to Wood
- Because veneers are applied on lighter base boards rather than being used as solid timber, they are lighter and easier to handle during installation. This makes them especially suitable for large furniture items, wall paneling, or ceiling treatments where weight could otherwise be a concern.
Limitations of Veneers:
- Requires Maintenance and Polishing
- Unlike laminates, veneers are made of real wood layers, which means they require regular maintenance and occasional polishing to retain their natural shine and texture. In material comparisons, this upkeep is a significant consideration, as it demands both time and care to prevent the surface from looking worn over time.
- Can Get Scratched Easily
- Although veneers provide the authentic look of wood, they are more susceptible to scratches and dents than solid wood. Daily use in high-traffic areas like kitchens, dining tables, or office furniture can result in surface marks, making careful handling and protective finishes important in material comparisons.
- Not as Durable as Solid Wood
- Veneers, while visually appealing, do not match the long-term durability of solid wood. In material comparisons, veneers are generally rated as medium-lifespan materials—they can last for years with proper care but are prone to damage from moisture, heavy impact, or sharp objects. This contrasts with solid wood, which can be sanded, repaired, and refinished multiple times over decades.
Applications: Wardrobe shutters, wall paneling, office tables, TV units, decorative furniture.
Veneers provide homeowners the luxury feel of wood without breaking the bank. They strike a balance between cost and elegance.
Glass: Modern and Elegant
Glass has become a key material in contemporary interiors. From partitions to tables and even wardrobes, glass adds openness and sophistication. In material comparisons, glass is unmatched for aesthetics but demands higher care.
Advantages of Glass:
- Adds openness, light, and luxury to interiors
- Available in clear, frosted, stained, and tinted options
- Easy to wipe and clean
- Works well in modern and minimal designs
Limitations of Glass:
- Fragile and prone to breakage
- Needs constant cleaning to avoid fingerprints and smudges
- Offers less privacy unless frosted
Applications: Sliding wardrobes, tabletops, bathroom enclosures, partitions, display units.
Glass furniture and features are perfect for urban homes seeking a premium touch, but families with children may find it less practical.
Metal: Strong and Stylish
Metal is gaining popularity in modern homes for its durability and edgy style. In material comparisons, metal is versatile because it works in both industrial and luxury interiors.
Advantages of Metal:
- Extremely durable and long-lasting
- Resistant to termites and moisture
- Can be molded into sleek or bold designs
- Complements industrial, modern, and eclectic styles
Limitations of Metal:
- Can feel cold and less inviting compared to wood
- Susceptible to rust if not treated
- Limited color choices compared to laminates
Applications: Bed frames, chairs, tables, open shelving, partitions, hardware.
Metal is best suited for contemporary spaces that prioritize strength, bold design, and low maintenance.
Discover trending metal and mixed-material furniture collections at InteriorGrid.com today.
Material Comparisons: A Quick Snapshot
- Wood: Luxurious, natural, but costly and high-maintenance
- Laminates: Affordable, versatile, but lacks authenticity
- Veneers: Natural appeal at a lower cost, moderate maintenance
- Glass: Elegant and modern, but fragile
- Metal: Durable, industrial, but limited warmth
Every home has unique needs. The right material depends on your budget, design preferences, and lifestyle. For example, a family with kids may choose laminates for durability, while a luxury apartment may opt for glass and wood combinations.
Conclusion
Making the right choice in interiors starts with clear material comparisons. Each material—wood, laminates, veneers, glass, and metal—has its strengths and weaknesses. By understanding these differences, homeowners can strike the right balance between aesthetics, durability, and budget. At the end of the day, the materials you choose should reflect not just trends, but also your personal lifestyle and long-term vision for your home.